What is age management?
Age management refers to management of human resources with an explicit focus on the requirement of an ageing workforce. Age management is holistic, intergenerational and life-course oriented.
Benefits of age management
Proactive management of age-diverse workforces is good for both workers and organisations. The benefits of age management for workers include:
- Better motivation;
- Greater job satisfaction;
- Better work-life balance;
- Increased performance of all age groups; and
- Maintained work ability and employability throughout the whole career.
The benefits and opportunities that age management offers to organisations are:
- Securing labour supply and anticipating skills/talent shortage;
- Avoiding the expensive loss of skills and experiences;
- Reduction in turnover and reduced costs for recruitment;
- Positive succession management when individuals do retire; and
- Taking full advantage of strengths and talents of different age groups, including tapping into the networks, expertise and experiences of mature workers.
Elements of age management
The following figure presents the different elements of age management. Below you can find short descriptions for each of the elements as well as links to further information.
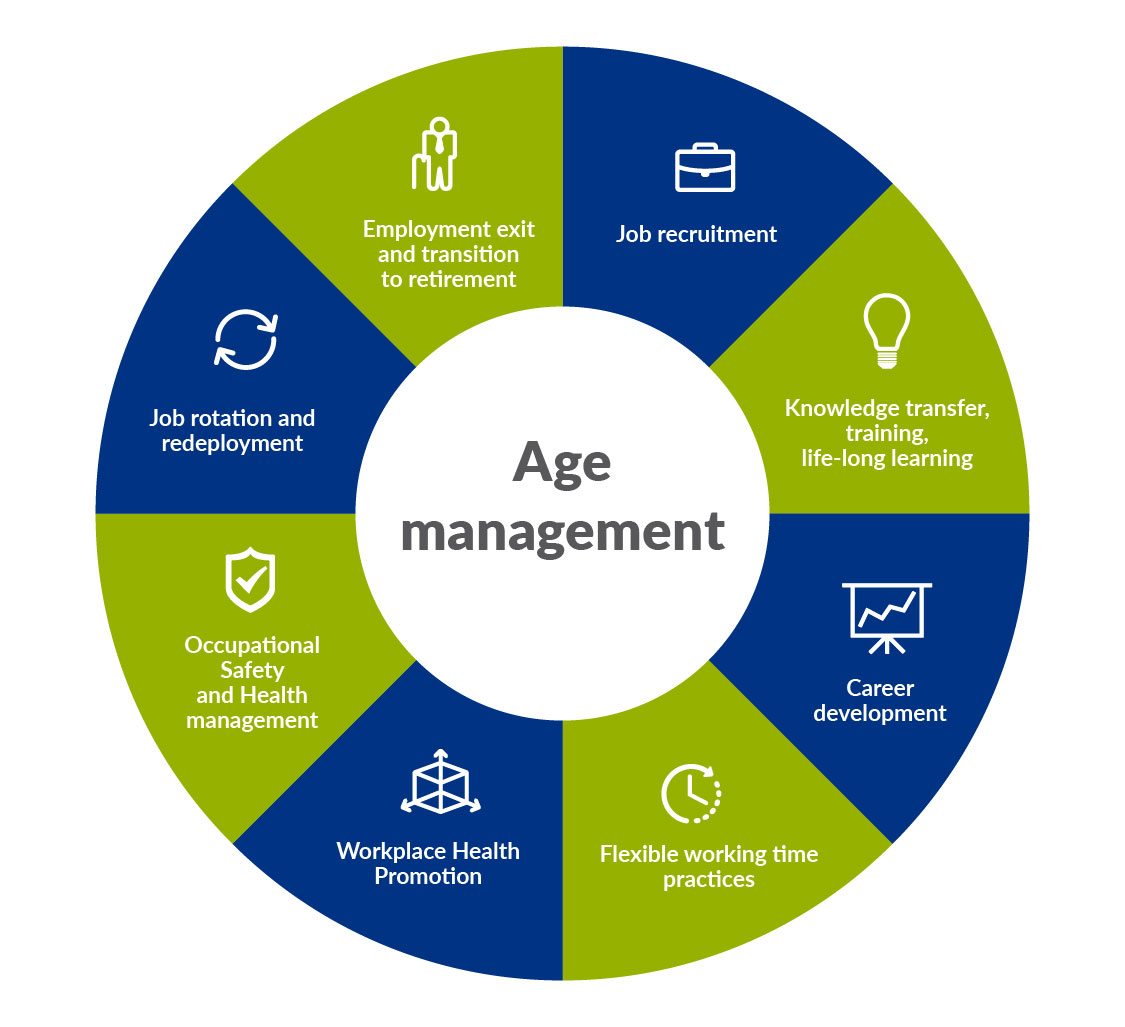
- Recruitment: Recruitment processes that focus on skills and experience, avoid age discrimination, and promote age diversity, bring many benefits to organisations. Read more (HR module).
- Knowledge transfer, training and life-long learning: Workers of all ages should have access to training and should be able to update their knowledge and skills. This is particularly relevant in the context of changing work practices and the introduction of new technologies. Read more (HR module).
- Career development: Career development should be seen in the context of the whole working life, ensuring a match between the job and the competences and capacities of the worker. Read more (HR module).
- Flexible working time practices: Flexible working time arrangements take into account the different needs of different age groups and help improve work-life balance. Read more (HR module).
- Workplace health promotion: Improving the work organisation and working environment, increasing workers' participation, and encouraging personal skills and professional development. Read more (next theme).
- Occupational safety and health management: Ensuring safety and health at work for workers of all ages through the implementation of age-sensitive risk assessments and adaptation of the workplace. Read more (next section).
- Job rotation and redeployment: Job design techniques in which workers are moved between two or more jobs in a planned manner at regular intervals. Read more (HR module).
- Employment exit and the transition to retirement: Supporting older workers in the planning of retirement. Read more (HR module).
The next section focuses on occupational safety and health management as part of age management, and discusses age-sensitive risk assessment and workplace adaptations.